The Cyber Onion
If you are familiar with the cybersecurity world, you may have noticed an explosion of new vendors and tools onto the market. The terminology and volume of ever changing acronyms can get pretty confusing, pretty quick. To try and understand the big picture, I like to break down the strategy, risks, and responses into the Cyber Onion. This approach thinks about risk and response on different levels, then applies tools and strategies to the level of risk.
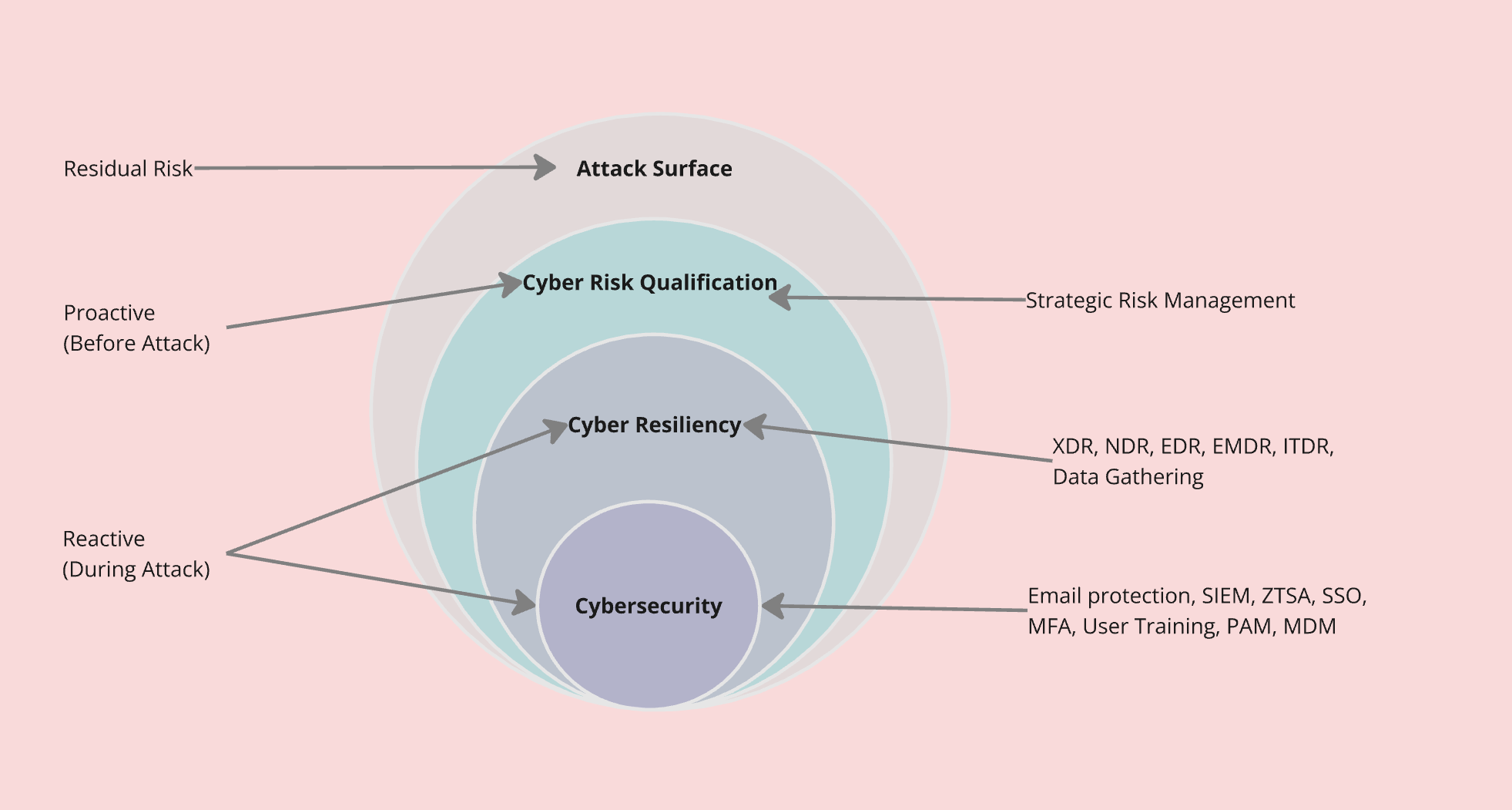
1. Attack Surface
The out layer contains your organization's Residual Risk, this is the risk that always remains no matter what you do to identify and eliminate risks. Hackers are always going to attempt an attack, internal employees are always prone to human error.
2. Risk Identification and Strategy
Risk identification and analysis can proactively identify, create awareness of and create response strategies to internal and external attack vectors.
Examples include:
- Strategic Identification of external and internal risks
- A risk register can be used in any size of organization to keep track of current risks and remediation plans.
- Cyber Insurance to cover identified Cyber Risk
- Messaging from the leadership team on Cyber Security
3. Cyber Resiliency
Risk detection, response, and mitigation. These tools are reactive to triggers for identified abnormal behaviour in your organization. Many tools have an automated response mechanisms and can mitigate risks and attacks from spreading further once they have begun in your organization. Examples include:
- Data gathering and analysis
- End Point Protection Solutions
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
- NDR (Network Detection and Response)
- EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response)
- EMDR (Email Detection and Response)
- ITDR (Identity Threat Detection and Response)
4. Cyber Security
The day to day continuous monitoring and management of risks, policies, programs, training and tools to ensure your organization meets an expected base standard of cyber security. Risk appetites can be defined along with normal and abnormal behaviours.
Examples include:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
- ZTSA (Zero Trust Security Architecture)
- MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)
- PAM (Privileged Access Management)
- SSO (Single Sign on)
- MDM (Mobile Device Management)
- Password Protection
- Email Protection
- End user training on Phishing and Cyber Security
About The Author
Lynsey Dunn is an IAM Consultant and Certified Okta Consultant at Distology Studios, bringing extensive Risk Analyst experience from previous positions at Deutsche Bank and Morgan Stanley.
Our website uses only technically necessary cookies. For more information visit our privacy policy.